In recent years, ancient grains have witnessed a resurgence in popularity as people seek out nutritious and wholesome foods. These remarkable grains, cultivated for centuries and largely untouched by modern genetic modification, offer a treasure trove of incredible health benefits.
From brown rice and khorasan wheat to black rice and spelt, ancient grains bring a variety of flavors, textures, and nutrients to our plates. In this comprehensive blog post, we will dive into the fascinating world of ancient grains, exploring their origins, nutritional profiles, and the vast array of health benefits ancient grains provide. So, let’s embark on a journey through time to uncover the extraordinary potential of these remarkable ancient grains.
Introduction to Ancient Grains
A. Defining Ancient Grains and Their Significance:
Ancient grains refer to a group of grains that have been cultivated for thousands of years and have remained largely unchanged by modern genetic modification.
These grains have deep historical roots and are valued for their exceptional nutritional profiles, unique flavors, and diverse culinary applications. What sets ancient grains apart from modern grain varieties is their ability to thrive in traditional agricultural systems, adapt to various climates, and withstand harsh growing conditions.
Ancient grains are characterized by their intact bran, germ, and endosperm, which provide a wealth of essential nutrients, including fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Their unaltered genetic makeup contributes to their distinct flavor profiles and desirable nutritional properties. These grains are often celebrated for their high fiber content, which promotes digestive health, regulates blood sugar levels, and supports weight management.
Many of these grains are found in our list of the 50 best high fiber foods to eat.
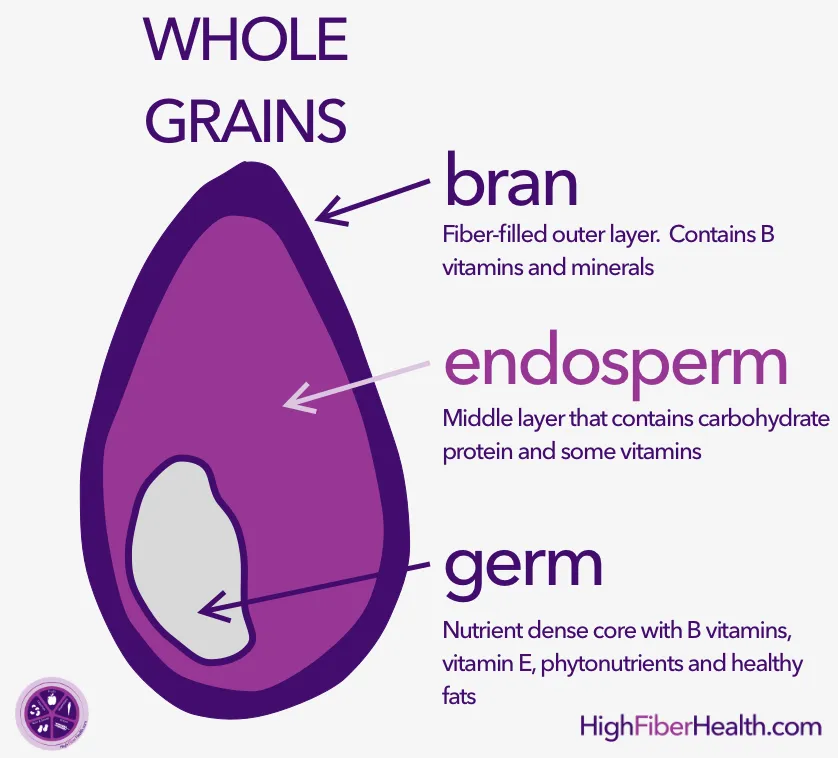
B. Ancient Grain Varieties and Their Geographical Origins:
Ancient grains encompass a wide range of varieties, each originating from different regions around the world. Some notable ancient grain varieties include:
- Quinoa from South America,
- Amaranth from Central America,
- Teff from East Africa,
- Spelt from Europe,
- Farro from the Mediterranean.
- Others include millet, sorghum, kamut, and freekeh.
The geographical origins of these grains reflect the historical and cultural practices of the regions where they were first cultivated. They often served as staple foods in these societies, providing sustenance and nourishment for generations. Ancient grain varieties have thrived in diverse climates, ranging from the arid lands of the Middle East to the high altitudes of the Andes, demonstrating their adaptability and resilience.
C. Historical Importance and Cultural Significance of Ancient Grains:
Ancient grains hold immense historical importance as they have been cultivated and consumed for thousands of years. These grains played a vital role in the diets of ancient civilizations and were regarded as sacred or essential foods in many cultures. They have been passed down through generations, carrying the traditions, flavors, and cultural significance of the communities that cultivated them.
For example, quinoa, a staple crop of the Incas, was considered a sacred grain and was integral to their agricultural and religious practices. Similarly, spelt was a staple grain in ancient Roman and medieval European diets, and its cultivation contributed to the development of these civilizations. The cultural significance of ancient grains can still be seen today in traditional dishes, festivals, and culinary practices around the world.
Understanding the defining characteristics, geographical origins, and historical significance of ancient grains helps us appreciate their value beyond their nutritional benefits. These grains connect us to our collective past, celebrate cultural diversity, and remind us of the deep-rooted relationship between humans and the crops that have sustained us for millennia.
Nutritional Powerhouses: Exploring the Nutrient Profiles of Ancient Grains
A. High Fiber Content: The Key to Digestive Health
One of the standout features of ancient grains is their high fiber content. Fiber plays a crucial role in promoting digestive health by aiding in proper bowel function, preventing constipation, and supporting a healthy gut microbiome.
Ancient grains like quinoa, amaranth, and teff are particularly rich in dietary fiber, with some varieties containing even higher amounts than modern grain counterparts. The insoluble fiber present in these grains adds bulk to the stool, facilitating its movement through the digestive tract and promoting regularity. Meanwhile, soluble fiber acts as a prebiotic, providing nourishment for beneficial gut bacteria, which in turn supports gut health and overall well-being.
B. Essential Vitamins and Minerals: Unleashing the Nutritional Value
Ancient grains are nutritional powerhouses, packed with essential vitamins and minerals that contribute to overall health. These grains are abundant sources of B vitamins, including thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, and folate, which are vital for energy production, nervous system function, and cell growth.
Additionally, they often contain minerals such as iron, magnesium, zinc, and phosphorus, which play key roles in numerous bodily processes, including immune function, bone health, and oxygen transport. Some varieties like quinoa and amaranth, are particularly notable for their high iron content, making them excellent choices for individuals with iron-deficiency anemia.
C. Complete Protein Source: Essential Amino Acids for a Balanced Diet
While ancient grains are not typically considered complete protein sources on their own, they often complement plant-based diets by providing a variety of essential amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein and are crucial for tissue repair, muscle growth, and hormone production.
Quinoa stands out as an exceptional ancient grain, as it contains all nine essential amino acids, making it a complete protein source. Amaranth and teff also offer a good balance of amino acids. By incorporating these grains into meals, individuals can enhance the protein quality of plant-based diets and meet their nutritional needs more effectively.
D. Healthy Fats and Fatty Acids: Nourishing the Body
Ancient grains can contribute to a well-rounded diet by providing healthy fats and essential fatty acids. While the fat content in ancient grains is generally low, it consists mainly of unsaturated fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. These fats have been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease and inflammation.
Additionally, certain ancient grains, such as chia seeds and amaranth, contain omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for brain health, reducing inflammation, and supporting cardiovascular health. Including ancient grains in a balanced diet provides a natural source of healthy fats that can contribute to overall well-being.
E. Antioxidant-Rich: Shielding Against Free Radicals
Antioxidants are compounds that help protect the body against damage caused by free radicals, unstable molecules that can contribute to chronic diseases and aging.
Ancient grains are known for their antioxidant content, which is due to the presence of various compounds such as phenolic acids, flavonoids, and anthocyanins. These antioxidants have been linked to a range of health benefits, including reduced inflammation, improved heart health, and a lower risk of certain cancers.
Black rice, for example, contains higher levels of anthocyanins compared to other rice varieties, giving it a deep purple hue and potent antioxidant properties. By incorporating antioxidant-rich ancient grains into our diet, we can support our immune system and defend against oxidative stress.
Incorporating ancient grains into our meals allows us to tap into their incredible nutritional potential. From their high fiber content for digestive health to their abundance of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, these grains offer a wealth of benefits.
They serve as a valuable addition to a balanced diet, providing essential nutrients, supporting overall well-being, and promoting optimal health.
Health Benefits of Ancient Grains
A. Heart Health: Lowering Cholesterol and Reducing Heart Disease Risk
Ancient grains have been associated with improved heart health due to their high fiber content and beneficial nutrients. The soluble fiber found in grains like oats, barley, and quinoa helps lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels by binding to cholesterol and preventing its absorption into the bloodstream.
By reducing LDL cholesterol, ancient grains can help prevent the buildup of plaque in the arteries and reduce the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Additionally, some ancient grains, such as amaranth and teff, contain compounds like phytosterols that further promote heart health by inhibiting cholesterol absorption.
B. Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining Stable Glucose Levels
For individuals concerned about blood sugar control, ancient grains offer a favorable option. These grains generally have a lower glycemic index compared to refined grains, meaning they have a gentler impact on blood sugar levels.
The high fiber content in ancient grains slows down the absorption of carbohydrates, preventing rapid spikes in blood sugar. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those seeking to manage their blood sugar levels.
Grains like quinoa, buckwheat, and amaranth have shown promising results in stabilizing blood glucose levels and improving insulin sensitivity.
C. Weight Management: Promoting Satiety and Supporting Weight Loss
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for overall well-being, and ancient grains can play a role in weight management. The combination of fiber, protein, and complex carbohydrates provides a satisfying and nourishing meal that promotes feelings of fullness and reduces the likelihood of overeating.
The high fiber content not only adds bulk to the diet but also slows down digestion, prolonging the feeling of satiety.
Additionally, the protein content helps preserve lean muscle mass during weight loss, which is important for maintaining a healthy metabolism.
D. Digestive Health: Boosting Gut Health and Bowel Regularity
The fiber-rich nature of ancient grains makes them excellent for digestive health. The insoluble fiber present in grains like bulgur, brown rice, and farro adds bulk to the stool and promotes regular bowel movements, preventing constipation and promoting overall bowel regularity.
Moreover, the prebiotic fibers found in certain ancient grains, such as inulin in spelt and resistant starch in barley, act as food for beneficial gut bacteria, supporting a healthy gut microbiome. A balanced and diverse gut microbiome has been linked to improved digestion, enhanced nutrient absorption, and even a strengthened immune system.
E. Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Combating Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is associated with various health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Ancient grains, particularly those rich in antioxidants and phytochemicals, possess anti-inflammatory properties that can help combat chronic inflammation.
The antioxidants present in grains like quinoa, amaranth, and millet help neutralize harmful free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in the body. The polyphenols and flavonoids found in ancient grains have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects, contributing to overall health and disease prevention.
F. Gluten-Free Options: Catering to Celiac Disease and Gluten Sensitivities
For individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivities, ancient grains offer a range of gluten-free options. While modern wheat contains gluten, many ancient grains are naturally gluten-free, providing an alternative for those who need to follow a gluten-free diet.
Grains like quinoa, amaranth, buckwheat, and millet are excellent choices as they are safe for individuals with celiac disease or gluten intolerance. These gluten-free options allow individuals to enjoy a varied and nutritious diet while avoiding gluten-related symptoms and potential long-term health complications.
Ancient Grains in Action: Tips and Delicious Recipes
A. Cooking and Preparation Tips for Incorporating Ancient Grains
When it comes to cooking with ancient grains, a few tips can help you make the most of these nutritious ingredients:
1. Rinse and soak: Some ancient grains, such as quinoa and amaranth, have a natural coating called saponin that can impart a bitter taste. Rinse these grains thoroughly before cooking. Additionally, soaking certain grains overnight can help improve their digestibility and reduce cooking time.
2. Proper water-to-grain ratio: Different grains require varying amounts of water for cooking. Follow the recommended water-to-grain ratio on the packaging or use a 2:1 ratio for most. Adjust as needed based on personal preference for texture.
3. Experiment with flavors: Ancient grains have unique nutty flavors that can be enhanced with various seasonings. Add herbs, spices, and aromatics like garlic or onion to infuse the grains with additional taste. Consider cooking grains in vegetable or chicken broth for added depth of flavor.
B. Versatile Recipe Ideas for Breakfast, Lunch, and Dinner
Ancient grains can be incorporated into a wide range of meals throughout the day. Here are a few recipe ideas to get you started:
1. Breakfast:
– Quinoa Breakfast Bowl: Cook quinoa with almond milk, cinnamon, and a touch of honey. Top with fresh fruits, nuts, and a drizzle of nut butter.
– Amaranth Porridge: Simmer amaranth with coconut milk, vanilla extract, and a sprinkle of cinnamon. Serve with a dollop of Greek yogurt and your favorite fruit.
2. Lunch:
– Farro Salad: Toss cooked farro with roasted vegetables, feta cheese, and a lemon-herb dressing for a satisfying grain salad.
– Millet Stuffed Bell Peppers: Combine cooked millet with sautéed vegetables, herbs, and spices. Stuff the mixture into bell peppers and bake until tender.
3. Dinner:
– Quinoa Stir-Fry: Sauté cooked quinoa with a medley of colorful vegetables, tofu or shrimp, and a flavorful sauce for a quick and nutritious stir-fry.
– Buckwheat Noodles with Vegetables: Cook buckwheat noodles and toss with stir-fried vegetables, sesame oil, and a soy-ginger dressing for a satisfying noodle dish.
C. Exploring Ancient Grains in Baking and Desserts
Ancient grains can also be incorporated into baking and dessert recipes, adding a wholesome touch to your sweet treats:
1. Quinoa Chocolate Chip Cookies: Substitute a portion of the flour in your favorite chocolate chip cookie recipe with cooked quinoa for added texture and nutrition.
2. Spelt Banana Bread: Swap out all-purpose flour with spelt flour in your banana bread recipe for a nuttier flavor and improved nutritional value.
3. Amaranth Energy Bars: Combine popped amaranth, nuts, dried fruits, and honey or maple syrup to create delicious homemade energy bars.
4. Teff Pancakes: Use teff flour to make fluffy and nutritious pancakes. Serve them with fresh berries and a drizzle of maple syrup.
Experiment with these recipes and feel free to adapt them according to your taste preferences and dietary needs. There are endless possibilities for creating delicious and nourishing meals that can be enjoyed by the whole family.
Conclusion :
Ancient grains, such as brown rice, khorasan wheat, spelt, and black rice, have captivated the attention of health-conscious individuals worldwide. With their rich nutritional profiles, distinct flavors, and versatile culinary applications, these grains have become an essential component of a balanced and wholesome diet.
From promoting heart health and aiding in weight management to supporting digestive wellness and offering anti-inflammatory benefits, ancient grains have proven their worth as nutritional powerhouses.
So, whether you savor the nutty taste of spelt or indulge in the vibrant hues of black rice, let these ancient wonders nourish your body and delight your taste buds. Embrace the past, unlock the health potential, and elevate your meals with the incredible benefits of ancient grains today!