Introduction
Maintaining a healthy diet is crucial for overall well-being, and one essential aspect of a healthy diet is ensuring an adequate dietary fiber intake. High-fiber beverages have become increasingly popular as a convenient, flavorsome way to supplement fiber consumption. This blog post will explore the advantages and considerations of incorporating high-fiber beverages into your daily routine. Specifically, we will explore their potential to positively impact heart disease prevention, weight management, and digestive health as well as the potential drawbacks associated with these beverages.
The Importance of Dietary Fiber for Great Health
Before delving into the pros and cons of high-fiber beverages, it’s vital to understand the significance of fiber in our diet. Fiber is a type of carbohydrate predominantly found in plant-based foods and is divided into two main categories: insoluble fiber and soluble fiber. Insoluble fiber aids in maintaining regular bowel movements by adding bulk to stool, while soluble fiber dissolves in water to form a gel-like substance, regulating blood sugar and cholesterol levels. Most Americans, over 92%, don’t get enough daily fiber. Using high-fiber beverages to supplement a well-rounded diet is an easy way to top off your dietary fiber intake.
Pros of Drinking High Fiber Beverages Daily.
1. Promotes Heart Health: High fiber intake, particularly soluble fiber, has been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease. Soluble fiber helps lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, thus reducing the likelihood of plaque buildup in the arteries, ultimately promoting cardiovascular health.
2. Aids in Weight Management: High-fiber foods and beverages are pivotal in weight loss and weight management. By incorporating these options into your diet, you can enjoy foods that are typically low in calories while still feeling satisfied. The fiber content adds volume and a sense of fullness, helping control appetite and potentially reducing overall calorie intake. To learn more about how dietary fiber can aid in weight loss, see our article on how dietary fiber acts as a natural GLP-1 agonist.
3. Supports Digestive Health: Consuming adequate fiber is crucial for maintaining a healthy digestive system. Insoluble fiber adds bulk to stool, preventing constipation and promoting regular bowel movements. Soluble fiber acts as a prebiotic, nourishing beneficial gut bacteria and fostering a balanced and healthy gut microbiome.
4. Assists in Blood Sugar Control: Soluble fiber plays a vital role in regulating blood sugar levels by slowing down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. This benefit is particularly important for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition, as it helps maintain stable blood sugar levels and promotes overall metabolic health.
Cons and Considerations
1. Added Sugar Content: Some high-fiber drinks, such as fruit drinks and smoothies, may contain added sugars that can contribute to excess calorie intake. Choosing beverages with minimal added sugar is essential to maintain the health benefits associated with high-fiber beverages. Reading labels and being mindful of the sugar content is crucial when selecting high-fiber beverages. Every diet that works has two things in common: high fiber and low sugar.
2. Nutritional Value: While high-fiber beverages provide fiber, they may lack the comprehensive nutritional profile of whole foods. Relying solely on these beverages can lead to a potential nutrient imbalance if they replace whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and other fiber-rich foods in the diet. Maintaining a diverse and balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods alongside high-fiber beverages is crucial.
3. Digestive Discomfort: Increasing fiber intake abruptly, mainly through concentrated sources or fiber supplements, can lead to bloating, gas, and other digestive discomforts. Gradually increasing fiber intake and ensuring adequate fluid consumption can help alleviate these symptoms.
4. Individual Variations: It’s essential to recognize that dietary fiber needs and tolerance levels vary among individuals. Certain medical conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome, may require careful consideration of fiber intake. Seeking personalized advice from healthcare professionals or registered dietitians can provide tailored recommendations based on individual needs and circumstances.
Examples of High Fiber Beverages:
There are several common high-fiber beverages available that can be easily incorporated into your daily routine. Here are a few examples:
1. Fruit Smoothies: Blending whole fruits, such as berries, bananas, and oranges, with a liquid base like almond milk or plain yogurt can create a delicious and fiber-rich beverage. Be sure to include the skin and pulp of the fruits to maximize fiber content.
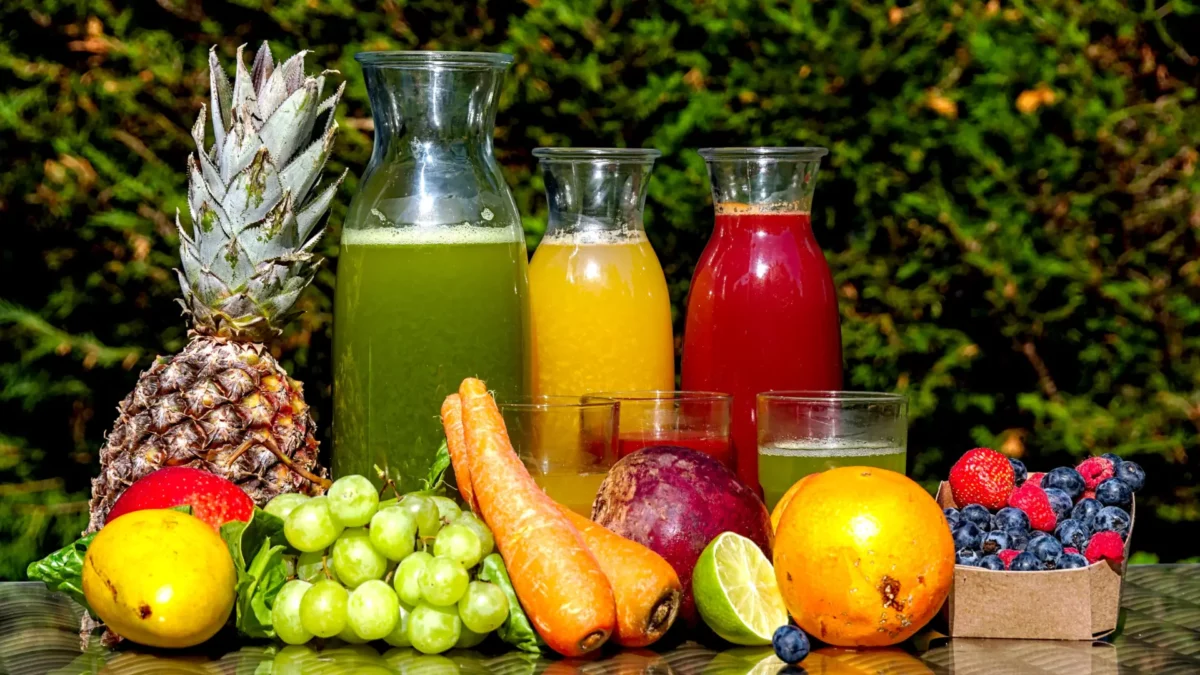
2. Some Vegetable Juices: Drinking vegetable juices, such as carrot, beet, or spinach juice, provides a concentrated source of fiber. You can either make your own at home using a juicer or choose commercially available options with no added sugars or preservatives.
3. Prune Juice: Prune juice is renowned for its high fiber content and natural laxative properties. It is an excellent choice for individuals looking to promote regular bowel movements and improve digestive health.
4. High-Fiber Protein Shakes: Some protein shake mixes and supplements are enriched with added fiber, making them a convenient option for increasing protein and fiber intake. Look for those labeled explicitly as high in fiber.
5. Chia Seed Water: Chia seeds are a fantastic source of soluble and insoluble fiber. Simply soaking chia seeds in water for a few minutes forms a gel-like consistency that can be enjoyed as a refreshing, fiber-packed beverage.
6. Psyllium Husk Drinks: Psyllium husk is a popular source of dietary fiber. It is available in powdered form and can be mixed with water or other liquids to create a high-fiber beverage. Follow the recommended dosage instructions for safe consumption.
7. Unsweetened Almond Milk: Almond milk, particularly the unsweetened variety, contains some natural fiber content. While the amount may vary, it can be suitable for those seeking a dairy-free, high-fiber alternative to regular milk.
8. Herbal Teas: Certain herbal teas, such as dandelion root tea or nettle tea, contain natural fibers and can contribute to your overall fiber intake. They offer a warm and soothing beverage option while providing additional health benefits.
Remember to check labels and choose beverages with minimal added sugars and no artificial additives. It’s also essential to prioritize whole foods as the primary source of dietary fiber and use high-fiber beverages to complement a well-rounded, fiber-rich diet.
Low Fiber Juices to Avoid
While juices are generally known for their fiber content, a few options are surprisingly low in fiber. Here are some examples:
1. Apple Juice: Apple juice is often filtered or clarified to remove the pulp and fiber, resulting in a low-fiber content juice. However, it is essential to note that cloudy apple juice or apple juice with pulp will contain more fiber, be sure to read the label to confirm the fiber content.
2. Grape Juice: Like apple juice, grape juice is typically strained to remove the fiber-rich grape skins and seeds, making it low in fiber.
3. Cranberry Juice: Cranberry juice is naturally low in fiber, especially if processed and strained to remove the cranberry solids.
4. Pineapple Juice: Pineapple juice is generally filtered to remove the fibrous core and pulp, making it relatively low in fiber.
5. Orange Juice (strained): While fresh orange juice contains some fiber, commercial orange juice that has been strained or clarified will have a reduced fiber content.
It’s important to note that these juices are low in fiber and high in sugars. For optimal health, it’s recommended to consume whole fruits and vegetables, which provide a higher fiber content and additional nutrients than their juice counterparts.
The Best Kept Secret for Beverages High in Dietary Fiber
Olipop is a popular high-fiber drink that has gained attention for its potential health benefits. Here are some reasons why you might consider incorporating Olipop into your diet
1. High Fiber Content: Olipop is specifically formulated to be rich in dietary fiber. Each can of Olipop contains approximately 9 grams of fiber, a significant portion of the recommended daily intake. Adequate fiber intake is associated with various health benefits, including improved digestion, weight management, and reduced risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes.
2. Prebiotic Benefits: Olipop contains prebiotic fiber, such as chicory root and Jerusalem artichoke, which act as food for the beneficial bacteria in your gut. These fibers promote the growth of good bacteria, leading to a healthy gut microbiome. A balanced gut microbiome is linked to better digestion, enhanced immune function, and improved mood and mental health.
3. Low Sugar Content: Unlike many other carbonated beverages, Olipop is formulated with low sugar levels. It contains only 2-5 grams of natural sugar per can, significantly lower than traditional soda or other sweetened beverages. This makes Olipop a healthier alternative for those looking to reduce their sugar intake without sacrificing flavor.
4. Natural Ingredients: Olipop has natural ingredients, including botanical extracts, fruit juices, and plant-based sweeteners. It is free from artificial additives, flavors, and colors, making it a cleaner and more wholesome option than many other carbonated drinks.
5. Variety of Flavors: Olipop offers a range of delicious flavors, such as Vintage Cola, Ginger Lemon, Strawberry Vanilla, and more. With its diverse flavor options, Olipop provides a refreshing and enjoyable alternative to conventional sugary sodas, helping you stay hydrated while enjoying a flavorful beverage.
6. Convenience and Portability: Olipop comes in a convenient canned form, making it easy to grab on the go or enjoy any time. Whether at work, running errands, or simply looking for a refreshing drink, Olipop provides a convenient option that fits your busy lifestyle.
It’s important to note that while Olipop can be a beneficial addition to your diet, it should not replace whole foods and other high-fiber sources in your meals. It is best to incorporate Olipop into a balanced and varied diet with a wide range of nutrient-dense and fiber-rich whole foods. As with any dietary changes or new products, it’s advisable to consult with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to ensure that Olipop aligns with your individual nutritional needs and health goals.
Conclusion
High-fiber beverages can be a convenient and delicious way to increase fiber intake and support overall health. They offer benefits like heart disease prevention, weight management, and improved digestive health. However, it is essential to choose beverages with minimal added sugars and to incorporate a variety of whole foods to ensure a well-rounded, nutrient-rich diet. Additionally, considering individual variations and potential digestive discomforts is essential. Striving for a healthy lifestyle should involve a balanced approach that includes a variety of high-fiber foods and beverages in conjunction with other essential nutrients.